Your cart is currently empty!

Heavy Metal Detox: Safeguarding Your Health from Environmental Toxins
Table of Contents
Heavy metals are naturally occurring elements that have a high atomic weight and a density at least five times greater than that of water. Their multiple industrial, domestic, agricultural, medical, and technological applications have led to a broad distribution in the environment; hence, they are a significant concern due to their toxicity at certain concentrations. Common heavy metals include lead, mercury, arsenic, cadmium, and aluminium, each with unique properties and uses. Unfortunately, the pervasive nature of these metals means they can be found in our water, air, soil, and even in the food we consume, posing a significant health risk over time.
How Heavy Metals Affect Human Health
The impact of heavy metals on human health is complex and varies depending on the type and concentration of the metal. Exposure to these metals, even in small amounts, can be toxic to humans, leading to acute and chronic health problems. They can accumulate in the body’s tissues, leading to a range of health issues such as neurological damage, respiratory problems, weakened immune systems, and in extreme cases, even cancer. Children and pregnant women are particularly vulnerable to the effects of heavy metal toxicity.
Importance of Detoxifying the Body from Heavy Metals
Given the widespread presence of heavy metals and their potential impact on health, it’s crucial to understand the importance of detoxification – the process of removing toxic substances from the body. Detoxification can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases, improve overall health, and enhance the body’s natural ability to heal and function. This article aims to explore the various aspects of heavy metal detoxification, including identifying sources of exposure, recognizing symptoms of toxicity, testing methods, and effective strategies for removing these metals from the body.
Identifying Common Heavy Metals and Their Sources

Lead: Sources and Effects
Lead, once commonly used in paints, gasoline, and plumbing pipes, is a highly toxic metal. Despite regulations limiting its use, lead remains a significant health concern, particularly in older homes and industrial areas. Common sources include lead-based paint, contaminated soil, old pipes, and some cosmetics and traditional medicines. Lead exposure can cause neurological problems, developmental delays in children, and kidney damage in adults.
Mercury: Sources and Effects
Mercury is primarily found in the environment due to industrial pollution and can accumulate in fish and shellfish, posing risks when consumed. It is also present in certain types of dental fillings, batteries, and fluorescent light bulbs. High levels of mercury exposure can impair neurological development, particularly in fetuses and young children, and cause symptoms like tremors, memory problems, and mood swings in adults.
Cadmium: Sources and Effects
Cadmium is a byproduct of industrial processes, particularly in the manufacturing of batteries, and is also found in some fertilizers and cigarettes. It can contaminate water and soil, subsequently entering the food chain. Cadmium exposure is linked to kidney damage, bone weakening, and an increased risk of cancer.
Arsenic: Sources and Effects
Arsenic, used in pesticides, wood preservatives, and also occurring naturally in high concentrations in some groundwater, is a potent carcinogen. It can be found in rice and rice-based products, seafood, and drinking water in certain areas. Chronic arsenic exposure can lead to skin lesions, cardiovascular diseases, and an increased risk of various cancers.
Others (Aluminum, Nickel, etc.): Sources and Effects
Aluminum, found in cookware, antiperspirants, and some vaccines, is generally considered safe in small amounts but may pose health risks with prolonged exposure. Nickel, used in stainless steel, coins, and electronic components, can cause allergic reactions and has been linked to lung and nasal cancers.
Symptoms and Health Risks Associated with Heavy Metal Exposure

Acute Symptoms
These can vary based on the metal but commonly include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, central nervous system dysfunction, muscle pain, and in severe cases, acute renal failure or coma. For example, acute lead poisoning can cause severe abdominal pain and neurological symptoms, while mercury poisoning may manifest as numbness or tingling in the hands and feet, and impaired speech or hearing.
Chronic Health Conditions
Chronic exposure to lower levels of heavy metals can lead to a range of long-term health issues. These include chronic kidney disease, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, cognitive decline, and increased risk of certain cancers. Heavy metals can accumulate in organs and tissues, causing oxidative stress and inflammation, which are key factors in the development of these chronic conditions.
Long-term Risks and Diseases
Long-term exposure to heavy metals can lead to more severe health conditions. For instance:
- Lead exposure can result in developmental disorders in children, reduced cognitive function, hypertension, and reproductive issues.
- Mercury is known for its neurotoxic effects, especially in developing fetuses, and can lead to neurological disorders and impaired cognitive function in adults.
- Cadmium exposure is strongly linked to renal failure, bone demineralization (osteoporosis), and an elevated risk of lung cancer.
- Chronic arsenic exposure has been associated with skin disorders, increased risk of skin, bladder, and lung cancers, and cardiovascular diseases.
These effects underscore the importance of understanding the potential impact of long-term heavy metal exposure and the necessity of measures to mitigate these risks.
Methods of Testing for Heavy Metal Toxicity
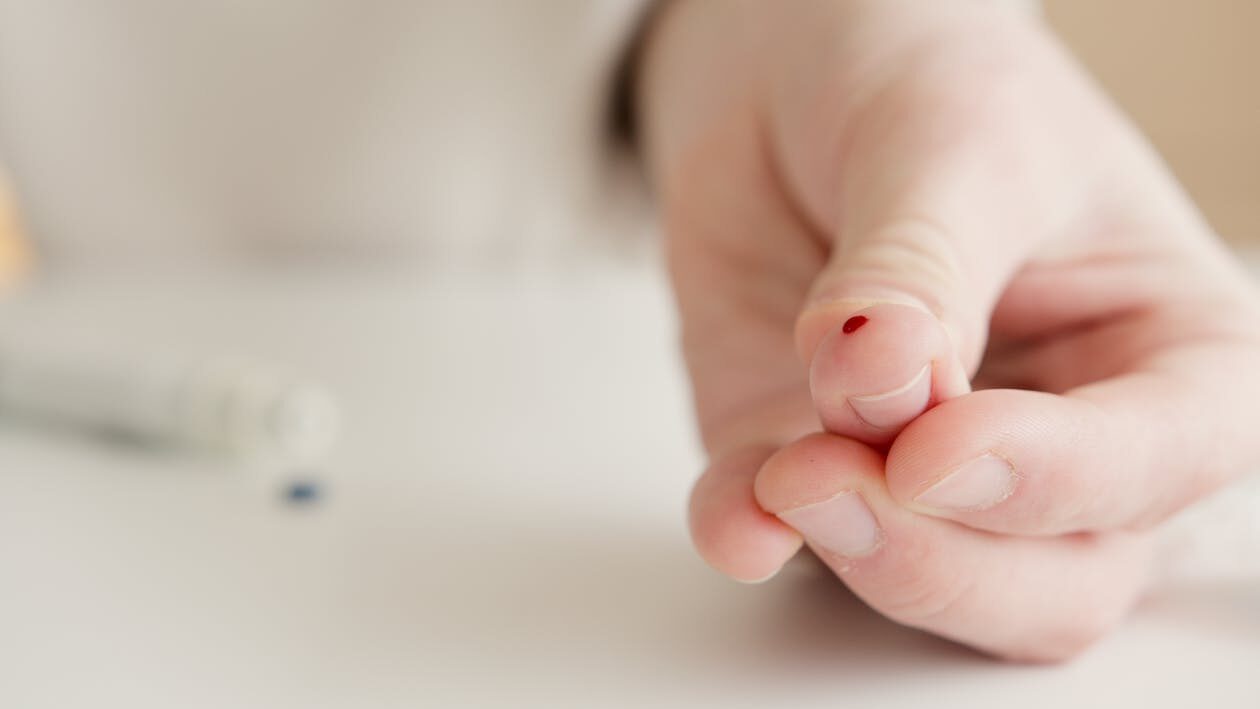
Blood Tests
Blood tests are commonly used to detect acute heavy metal poisoning. They are effective for assessing recent or ongoing exposure, especially for metals like lead, mercury, and cadmium. However, blood tests may not reflect past exposure or the total burden of metals accumulated in the body, as heavy metals often reside in tissues rather than circulating in the bloodstream.
Hair and Nail Analysis
Hair and nail analyses can provide a record of past exposure to heavy metals over a period of weeks to months. These tests are particularly useful for chronic exposure assessment, as heavy metals are deposited in the keratin of hair and nails. However, the interpretation of these tests can be complex and may require correlation with clinical symptoms and other tests.
Urine Tests
Urine testing is another effective method for detecting many heavy metals, including cadmium, mercury, and lead. Urine tests are often used to monitor exposure in industrial settings and can be utilized alongside chelation therapy to assess the excretion of metals. They are especially useful for evaluating the body’s excretion of metals after acute exposure.
Other Diagnostic Methods
Additional testing methods include stool analysis, which can be used to assess excretion of metals through the gastrointestinal tract, and X-rays, which can identify certain metals like lead in the body. Advanced imaging techniques and specialized laboratory tests may also be employed in specific cases to understand the extent of heavy metal burden and related health impacts.
Strategies for Heavy Metal Detoxification

Dietary Changes and Nutrition
- Foods to Avoid: Certain foods are known to be higher in heavy metals, such as large fish (which may contain mercury), non-organic produce (potential pesticide residue), and foods from areas known for heavy metal contamination. Reducing consumption of these can help lower overall exposure.
- Beneficial Foods and Supplements: Including foods rich in certain nutrients can aid in detoxification. These include fiber-rich foods, which help eliminate toxins through the digestive system, and foods high in antioxidants, like fruits and vegetables, which combat oxidative stress caused by metals. Supplements such as vitamin C, selenium, and zinc can also support detoxification processes.
Lifestyle Changes
- Reducing Exposure in the Environment: This involves identifying and minimizing contact with potential sources of heavy metals. Steps can include using water filters to reduce metal content in drinking water, choosing lead-free products and materials, and avoiding areas known to be contaminated with heavy metals.
- Safe Use of Household Products: Being mindful of the content of household items, such as cookware, cosmetics, and cleaning products, can reduce exposure. Opting for products with fewer chemicals and known contaminants is advisable.
Medical Treatments
- Chelation Therapy: This medical treatment involves the administration of chelating agents, which bind to heavy metals in the body and facilitate their excretion. It is used for treating acute and chronic metal poisoning but must be administered under medical supervision due to potential side effects and risks.
- Other Medical Interventions: Depending on the type and severity of metal toxicity, other treatments may include medications to alleviate symptoms, therapies to support affected organs (like the kidneys or liver), and ongoing monitoring and management of health conditions caused by metal exposure.
The Role of Natural Remedies in Heavy Metal Detox

Herbal Remedies
- Common Herbs Used for Detoxification: Certain herbs are known for their detoxifying properties. Cilantro, for example, is believed to help eliminate mercury and other heavy metals from the body. Chlorella, a type of algae, is another popular choice for its ability to bind to heavy metals and aid in their removal.
- How They Work in the Body: These herbs often work by binding to heavy metals in the bloodstream or the digestive tract, making them easier to be excreted from the body. They may also support liver and kidney function, which are crucial for detoxification processes.
Homeopathic Methods
- Principles of Homeopathy in Detox: Homeopathic remedies are based on the principle of treating ‘like with like’. These remedies, in highly diluted forms, are thought to stimulate the body’s natural healing processes.
- Popular Homeopathic Remedies: Remedies such as Sulphur, Silicea, and Calcarea Carbonica are sometimes recommended for detoxification, although scientific evidence supporting the efficacy of homeopathy in heavy metal detoxification is limited.
Detox Baths and Sauna Therapy
- Benefits of Detox Baths: Baths using Epsom salts, clay, or baking soda are believed to help draw out toxins through the skin. The warm water can also promote relaxation and improve circulation, aiding the body’s natural detoxification processes.
- Role of Sauna Therapy in Toxin Elimination: Sauna therapy, particularly infrared saunas, can induce sweating, a natural way for the body to eliminate toxins, including heavy metals. Regular sauna sessions are often recommended as a part of detoxification programs.
Supplemental Products: FoliumpX
- Overview of FoliumpX: FoliumpX is a unique dietary supplement designed to aid in the removal of heavy metals from the body. Comprising natural ingredients, including potent antioxidants and specific plant extracts, it’s crafted to support the body’s detoxification processes in a holistic manner.
- How FoliumpX Aids in Heavy Metal Detoxification: FoliumpX’s formula is engineered to synergize with the body’s natural detox pathways. The antioxidants in FoliumpX help to mitigate oxidative stress, a common byproduct of toxin exposure, while its active ingredients are known for their potential to bind to heavy metals, aiding in their safe and efficient elimination from the body.
Preventive Measures and Maintaining a Low-Toxin Lifestyle

Tips for Reducing Everyday Exposure
- Water Filtration: Using a high-quality water filter can help reduce exposure to heavy metals commonly found in drinking water.
- Organic Foods: Opting for organic produce can minimize exposure to pesticides and fertilizers that may contain heavy metals.
- Household and Personal Care Products: Choosing natural, non-toxic cleaning and personal care products can reduce daily exposure to various chemicals and potential heavy metals.
- Safe Cookware: Using cookware that is free of heavy metal leaching, such as ceramic or stainless steel, can prevent contamination of food during cooking.
Importance of Regular Testing and Health Check-Ups
Regular testing for heavy metal exposure, especially for those living in high-risk areas or working in certain industries, is crucial. Routine health check-ups can help monitor any potential effects of long-term exposure and ensure timely intervention if necessary.
Advocacy for Cleaner Environments and Regulations
- Community Involvement: Engaging in community efforts to address and reduce local pollution sources can have a significant impact on reducing heavy metal exposure.
- Supporting Regulations: Advocating for stricter regulations on industrial emissions and waste disposal can help minimize environmental contamination.
- Educational Outreach: Spreading awareness about the sources and risks of heavy metal exposure is key to public health and preventive measures.
Conclusion: Heavy Metal Detox
Heavy metal detoxification is a vital aspect of holistic health. By taking steps to minimize exposure, prioritizing regular health check-ups, and considering detoxification when necessary, individuals can empower themselves to protect their well-being in an increasingly polluted world.
As we look to the future, ongoing research and emerging treatments offer promise for more effective detoxification approaches. Additionally, advocating for environmental protection and stricter regulations is crucial, highlighting our collective responsibility for a healthier planet where both personal health and the well-being of our environment are inextricably linked.
Discover how FoliumpX can aid in your journey to detoxify and protect your body from heavy metals; learn more and start your path to better health today.
Further Reading
For further reading and resources on heavy metal detoxification, here are some recommendations.
Websites and Articles:
- Integrative Pain and Wellness Center: https://ipawc.com/health-and-wellness-blog/what-can-environmental-toxins-do-to-the-body
- Healthline: https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/food-toxins-that-are-concerning
- WebMD: https://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/what-is-heavy-metal-poisoning
Blogs and Social Media:
- The Detox Institute: This website features a blog with articles and resources on detoxification, including heavy metals, written by healthcare professionals and experienced practitioners. You can find them at https://thedetoxcenter.com.
- Dr. Axe: Dr. Josh Axe’s website and social media channels provide information and updates on natural health topics, including heavy metal detox. You can access his website at https://draxe.com/ and follow him on social media for relevant content.
Livestreams and Webinars:
- Institute for Functional Medicine: The Institute for Functional Medicine holds conferences and webinars throughout the year. Keep an eye on their website for upcoming events at https://www.ifm.org.
Leave a Reply